Compound Monthly Growth Rate (CMGR): A Complete Guide
Growth metrics are essential tools for measuring success and making strategic decisions in business and investments. Among these metrics, the Compound Monthly Growth Rate (CMGR) stands out for its ability to provide insights into consistent month-over-month growth. Whether you're an entrepreneur, investor, or financial analyst, understanding CMGR can empower you to gauge performance and make data-driven decisions.
This guide will take you through everything you need to know about CMGR: its formula, importance, practical applications, comparisons with other growth metrics, and best practices for leveraging it effectively. Let's dive in!
The Importance of CMGR in Financial Analysis
Why is CMGR so important? Financial analysis is all about understanding performance trends over time. CMGR helps businesses and investors uncover consistent growth patterns while accounting for the effect of compounding a critical factor in evaluating long-term performance.
Key Reasons Why CMGR is Crucial
- Consistency Measurement: It smoothens out fluctuations and provides a steady measure of growth over a defined period.
- Strategic Planning: Companies use CMGR to predict future growth and allocate resources accordingly.
- Performance Benchmarking: It allows comparison between different businesses or investments.
- Investor Insights: CMGR helps evaluate whether an investment or business strategy aligns with long-term growth objectives.
For instance, if you're a startup tracking user acquisition, CMGR can help you identify whether you're growing consistently or if there are periods of stagnation.
The Formula for Calculating CMGR
The CMGR formula is straightforward yet powerful. Here's how it looks:
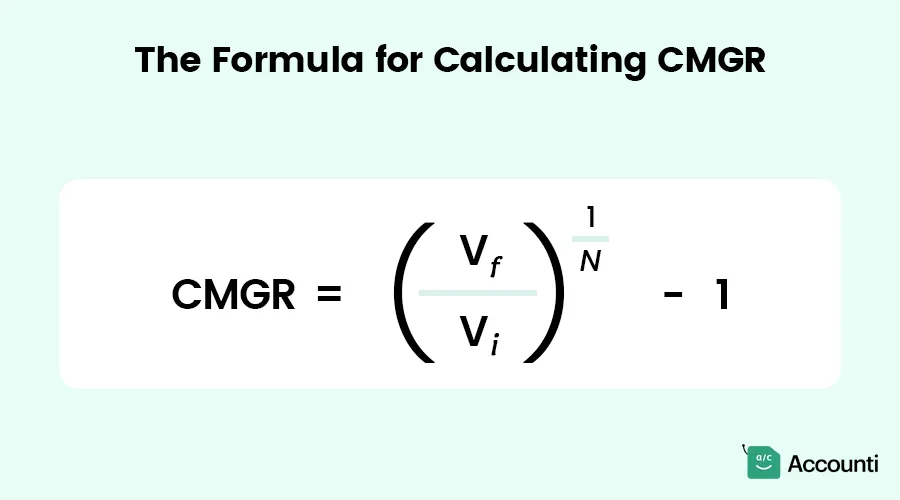
Breaking It Down:
- (V_f): The final value or ending amount (e.g., revenue, users, sales).
- (V_i): The initial value or starting amount.
- (N): The number of months in the time period.
Example Calculation
Suppose your company's revenue grew from $10,000 to $20,000 in 12 months. Here's how you calculate CMGR:
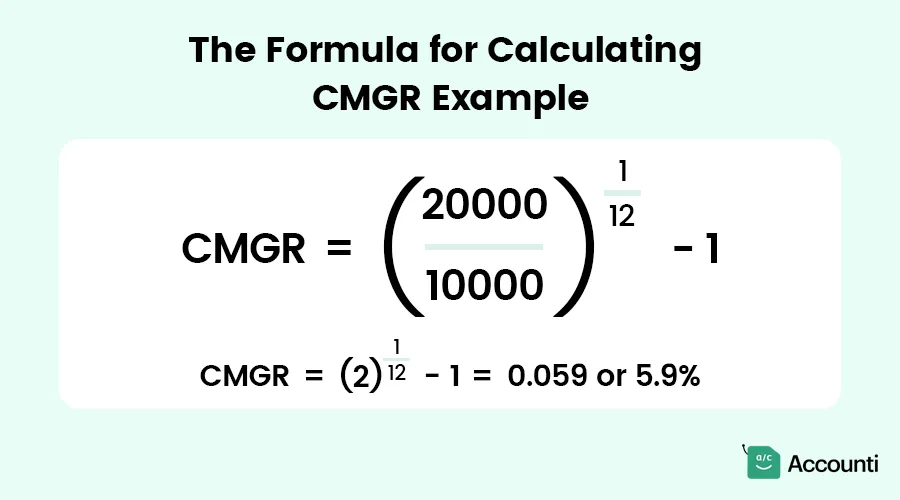
This means your revenue grew at an average rate of 5.9% per month.
Steps to Calculate CMGR
Let's break down the calculation process into actionable steps:
Step 1: Identify the Key Values
- Determine the starting value ((V_i)).
- Find the ending value ((V_f)).
- Count the number of months ((N)) over which the growth occurred.
Step 2: Plug Values Into the Formula
- Apply the formula (left( frac{V_f}{V_i} right)^{frac{1}{N}} - 1).
Step 3: Interpret the Result
- Convert the decimal result to a percentage for easy understanding.
- Use this percentage to communicate growth trends to stakeholders.
Applications of CMGR in Business
CMGR is widely used across industries to measure and forecast performance. Here are some practical applications:
1. Revenue Growth Analysis
Businesses use CMGR to assess month-over-month revenue increases and set financial goals.
2. Customer Acquisition
CMGR helps evaluate how quickly new customers or users are joining over time.
3. Subscription Services
For SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) companies, CMGR is key in tracking recurring revenue growth.
4. Marketing Campaigns
By applying CMGR to conversion rates, businesses can gauge the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
5. Investment Analysis
Investors use CMGR to evaluate the potential of a stock, fund, or portfolio over time.
CMGR vs. Other Growth Metrics
CMGR often gets compared to other growth metrics, such as Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) and Monthly Growth Rate (MGR). Let's see how it stacks up:
| Metric | Definition | Best Used For |
| CMGR | Average monthly growth rate, accounting for compounding effects. | Month-to-month analysis of short-term growth trends. |
| CAGR | Average annual growth rate over multiple years. | Long-term investment and business performance tracking. |
| MGR | Growth rate without considering compounding. | Quick, simple monthly growth insights. |
Key Difference
While CAGR focuses on annual growth, CMGR is more granular, offering insights into monthly performance. For businesses needing to monitor short-term trends, CMGR provides a clearer picture.
Best Practices for Using CMGR in Financial Analysis
To make the most of CMGR, follow these best practices:
1. Use Accurate Data
Ensure your initial and final values are precise to avoid skewed results.
2. Combine with Other Metrics
CMGR works best when paired with metrics like Net Profit Margin or Customer Retention Rate.
3. Regularly Monitor CMGR
Track it monthly to identify trends or changes in performance early on.
4. Leverage Tools
Use financial tools like Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized software to automate CMGR calculations.
5. Avoid Overgeneralization
While CMGR shows consistent growth, it may not reflect short-term volatility or seasonal trends.
Leverage CMGR for Strategic Growth Insights
By understanding CMGR, businesses can uncover key drivers of growth and create targeted strategies. For example:
- Forecast Revenue: Predict whether current growth rates align with long-term financial goals.
- Set KPIs: Establish key performance indicators based on CMGR trends.
- Identify Weaknesses: Use CMGR to spot underperforming areas and redirect resources.
Strategic use of CMGR empowers companies to optimize operations, achieve sustained growth, and stay ahead of competitors.
Conclusion
The Compound Monthly Growth Rate (CMGR) is an invaluable tool for understanding and leveraging growth trends in business and investments. Its ability to measure consistent growth, predict future performance, and guide strategic decisions makes it essential for any financial analysis toolkit. By following best practices and integrating CMGR with other metrics, businesses can unlock new opportunities and achieve sustained success.
FAQs
What is a good CMGR percentage for a startup?
A good Compound Monthly Growth Rate (CMGR) for startups, particularly in the Software as a Service (SaaS) sector, varies depending on the company's stage and industry. In the early stages, top-performing SaaS startups often experience monthly growth rates between 10% and 17%. As these companies mature and achieve an Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) exceeding $3 million, growth rates typically stabilize around 6% to 7% per month. On average, SaaS businesses grow approximately 2% to 2.5% monthly throughout their lifecycle.
What is a good monthly growth rate?
A good monthly growth rate is context-dependent, varying by industry, company size, and market conditions. For SaaS startups, a monthly growth rate of 5% to 15% is generally considered healthy. After reaching $1 million in ARR, maintaining a growth rate of 10% or higher is advisable. However, it's essential to consider factors such as churn rates, market saturation, and scalability when evaluating growth rates.
Can CMGR predict future growth?
While CMGR provides insights into a company's average monthly growth over a specific period, it is primarily a historical metric and does not inherently predict future growth. However, businesses can use CMGR to forecast future performance by analyzing past trends and making informed projections. It's crucial to consider other factors such as market dynamics, competition, and internal capabilities when using CMGR for future planning.
How does CMGR differ from CAGR?
CMGR (Compound Monthly Growth Rate) and CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) are both metrics used to measure growth over time, but they differ in their time frames and applications. CMGR calculates the average monthly growth rate over a specified period, making it suitable for short-term analysis. In contrast, CAGR measures the mean annual growth rate over a period longer than one year, providing a long-term perspective. The formula for CMGR is similar to CAGR but adjusted for monthly intervals.
How do you interpret compound annual growth rate?
The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) represents the mean annual growth rate of an investment over a specified period, assuming the investment has been compounding over that time. It provides a smoothed annual rate that helps investors understand the consistent rate of return required for an investment to grow from its beginning balance to its ending balance, assuming profits are reinvested each year. CAGR is particularly useful for comparing the historical performance of investments or assessing the growth of a company's revenue or other metrics over time.

 Rohit Kapoor
Rohit Kapoor

